FAQs
1. What is an ERGO PAD?
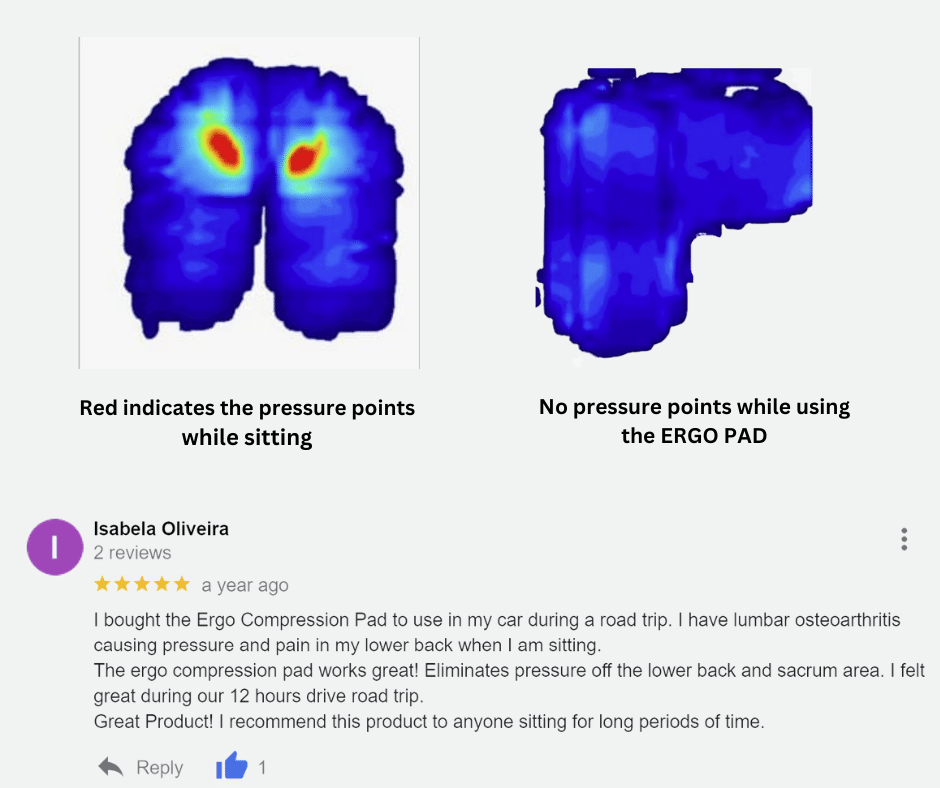
The ERGO PAD is the leading non-powered air pressure redistribution cushion. It is a clinically proven solution designed to redistribute pressure at bony prominences and achieve better comfort for sitting for long hours.
3. What is the ERGO PAD used for?
The Ergo Pad is a static air cushion featuring a recessed valve system that allows inflation tailored to the individual user’s needs. The ERGO PAD is used to relieve pressure from sciatica nerve issues and lower back pain due to long term sitting.
- What does the ERGO PAD do?
- The ERGO PAD protects the user by reducing the risk of pressure injuries and helps improve comfort when sitting.
- When properly inflated, the ERGO PAD lifts sit bones and tailbone off the surface.
- Allows the body to sink into the product, helping increase comfort.
- Unique venting holes provide airflow to keep the user comfortable.
- What if the ERGO PAD Deflates?
- Ergo Pad (A~flexX) Brand products have the best warranty in the business. If you suspect a manufacturer’s defect, call our Customer Service Department at 954 600-8664 . They will walk you through our inspection process. Or you can check the following conditions of your ERGO PAD product as our products can be repaired. Are the valves properly sealed? Sometimes the valve top isn’t sealed against the inflation port and a slow leak occurs.

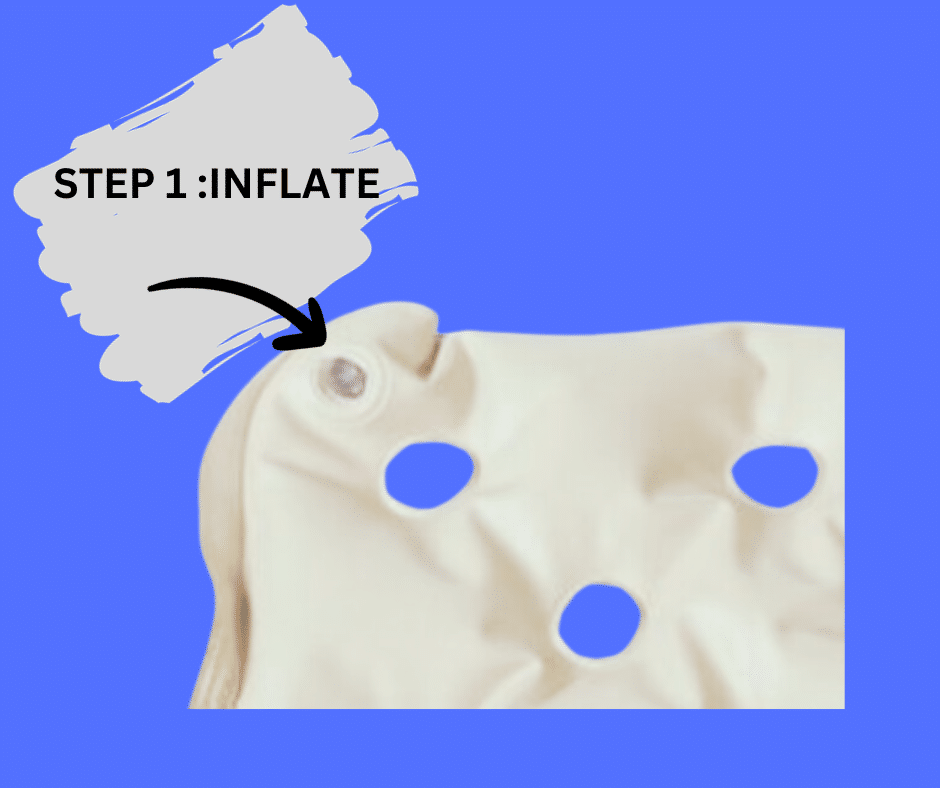
If additional air is required, insert the open valve and add more air, like blowing up a beach ball. Make sure that the stem is placed all the way back in .
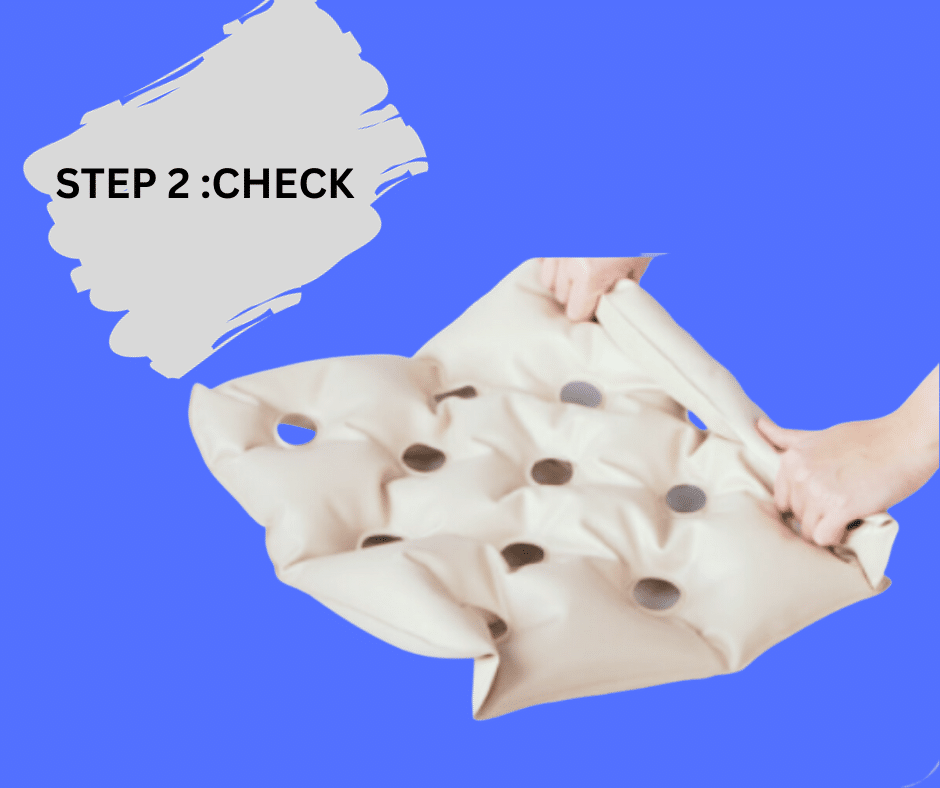
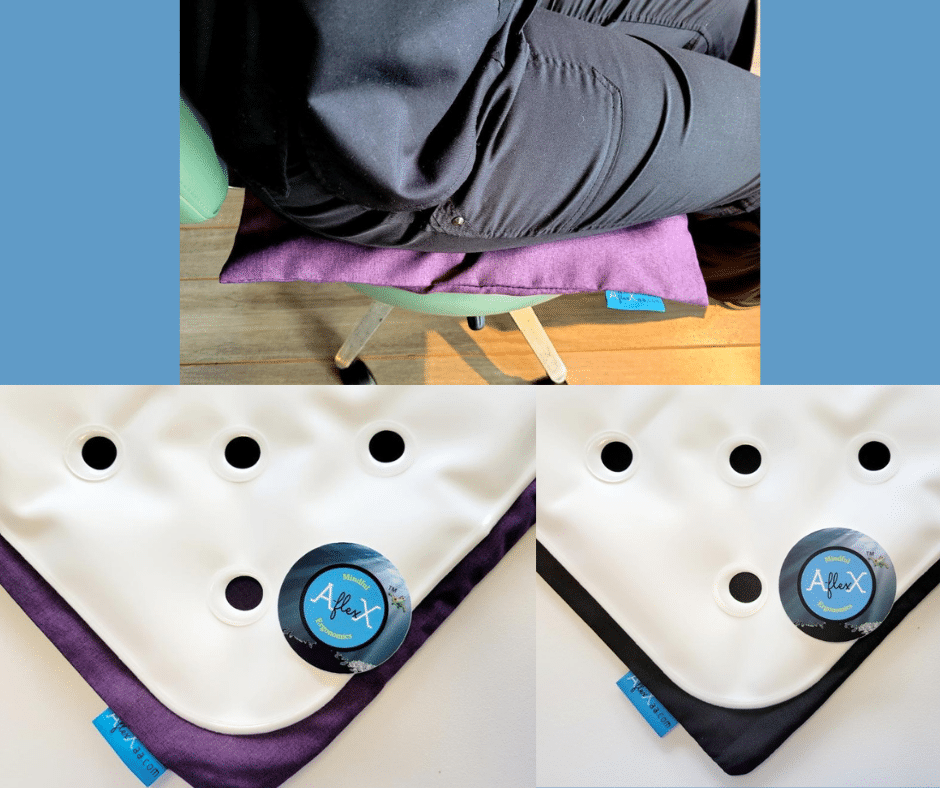
Once the cushion appears about 60% full, check for proper inflation. If you can easily roll one side of the product past the first set of holes but not to the second, your cushion is ready to use.
After you have checked the air pressure and it is just the amount needed, use your cushion. Place the valve side down, towards the back of the seating surface.